. Determine the access methods (console, Telnet, Port-Access (802.1X), SSH, and/or web browser interface) for which you want RADIUS as the primary authentication method. Consider both Operator (login) and Manager (enable) levels, as well as which secondary authentication methods to use (local or none) if the RADIUS authentication fails or does. Note that in the HP ProCurve implementation, a switch port can also be configuredas a supplicant, in order to secure links between network devices.The configuration of Windows XP and Vista supplicants for 802.1X is described in ProCurve Application Note AN-S3,How to configure 802.1X authentication with a Windows XP or Vista supplicant.HP. Note that in the HP ProCurve implementation, a switch port can also be configuredas a supplicant, in order to secure links between network devices.The configuration of Windows XP and Vista supplicants for 802.1X is described in ProCurve Application Note AN-S3,How to configure 802.1X authentication with a Windows XP or Vista supplicant.HP.
The switch can automatically configure a dynamic LACP trunk group, or you can manually configure a static LACP trunk group. Uniblue driverscanner 2019.
NOTE:LACP requires full-duplex (FDx) links of the same media type (10/100Base-T, 100FX, and so on) and the same speed and enforces speed and duplex conformance across a trunk group. For most installations, HP Switch recommends that you leave the port mode settings at |
LACP trunk status commands include:
| Trunk display method | Static LACP trunk | Dynamic LACP trunk |
|---|---|---|
CLI show lacp command | Included in listing. | Included in listing. |
CLI show trunk command | Included in listing. | Not included. |
| Port/Trunk Settings screen in menu interface | Included in listing. | Not included |
Thus, to display a listing of dynamic LACP trunk ports, you must use the show lacp command.
In most cases, trunks configured for LACP on the switches operate as described in LACP trunk types.
LACP trunk types
| LACP port trunk configuration | Operation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic LACP | This option automatically establishes an 802.3ad-compliant trunk group, with LACP for the port Type parameter and DynX for the port Group name, where X is an automatically assigned value from 1 to 60, depending on how many dynamic and static trunks are currently on the switch. (The switch allows a maximum of 60 trunk groups in any combination of static and dynamic trunks.)
Under the following conditions, the switch automatically establishes a dynamic LACP port trunk group and assigns a port Group name:
Either of the above link configurations allows a dynamic LACP trunk link. Backup Links:A maximum of eight operating links are allowed in the trunk, but, with dynamic LACP, you can configure one or more additional (backup) links that the switch automatically activates if a primary link fails. To configure a link as a standby for an existing eight-port dynamic LACP trunk, ensure that the ports in the standby link are configured as either active-to-active or active-to-passive between switches. Displaying dynamic LACP trunk data: To list the configuration and status for a dynamic LACP trunk, use the CLI
| ||
| Static LACP | Provides a manually configured, static LACP trunk to accommodate these conditions:
The trunk operates if the trunk group on the opposite device is running one of the following trunking protocols: This option uses LACP for the port Type parameter and TrkX for the port Group parameter, where X is an automatically assigned value in a range corresponding to the maximum number of trunks the switch allows. (The table on Trunk types used in static and dynamic trunk groups lists the maximum number of trunk groups allowed on the switches.) Displaying static LACP trunk data : To list the configuration and status for a static LACP trunk, use the CLI Static LACP does not allow standby ports. |
In the default configuration, LACP is disabled for all ports. If LACP is not configured as Active on at least one end of a link, the port does not try to detect a trunk configuration and operates as a standard, untrunked port. LACP port status data lists the elements of per-port LACP operation. To display this data for a switch, execute the following command in the CLI:
LACP port status data
| Status name | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
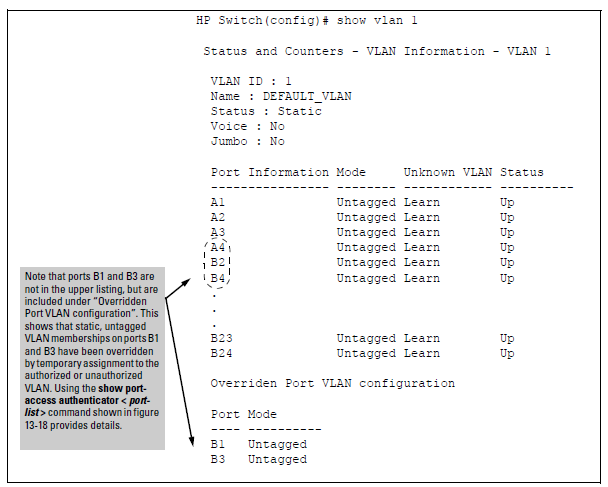
| Port Numb | Shows the physical port number for each port configured for LACP operation (C1, C2, C3 …). Unlisted port numbers indicate that the missing ports that are assigned to a static trunk group are not configured for any trunking. | |
| LACP Enabled | Active: The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets. Passive: The port does not automatically send LACP protocol packets and responds only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device. A link having either two active LACP ports or one active port and one passive port can perform dynamic LACP trunking. A link having two passive LACP ports does not perform LACP trunking because both ports are waiting for an LACP protocol packet from the opposite device.
| |
| Trunk Group | TrkX: This port has been manually configured into a static LACP trunk. Trunk group same as port number: The port is configured for LACP, but is not a member of a port trunk. | |
| Port Status | Up: The port has an active LACP link and is not blocked or in standby mode. Down: The port is enabled, but an LACP link is not established. This can indicate, For example, a port that is not connected to the network or a speed mismatch between a pair of linked ports. Disabled: The port cannot carry traffic. Blocked: LACP, Spanning Tree has blocked the port. (The port is not in LACP standby mode.) This may be caused by a (brief) trunk negotiation or a configuration error, such as differing port speeds on the same link or trying to connect the switch to more trunks than it can support. (See the table on Trunk configuration protocols.)
Standby: The port is configured for dynamic LACP trunking to another device, but the maximum number of ports for the dynamic trunk to that device has already been reached on either the switch or the other device. This port will remain in reserve, or 'standby' unless LACP detects that another, active link in the trunk has become disabled, blocked, or down. In this case, LACP automatically assigns a standby port, if available, to replace the failed port. | |
| LACP Partner | Yes: LACP is enabled on both ends of the link. No: LACP is enabled on the switch, but either LACP is not enabled or the link has not been detected on the opposite device. | |
| LACP Status | Success: LACP is enabled on the port, detects and synchronizes with a device on the other end of the link, and can move traffic across the link. Failure: LACP is enabled on a port and detects a device on the other end of the link, but is not able to synchronize with this device, and therefore is not able to send LACP packets across the link. This can be caused, For example, by an intervening device on the link (such as a hub), a bad hardware connection, or if the LACP operation on the opposite device does not comply with the IEEE 802.3ad standard. |
802.1X (Port-based access control) configured on a port
To maintain security, LACP is not allowed on ports configured for 802.1X authenticator operation. Chaos uk discography. If you configure port security on a port on which LACP (active or passive) is configured, the switch removes the LACP configuration, displays a notice that LACP is disabled on the port, and enables 802.1X on that port.
Hp Switch 802.1 X Configuration
The switch does not allow you to configure LACP on a port on which port access (802.1X) is enabled. For Example:
To restore LACP to the port, you must first remove the 802.1X configuration of the port and then re-enable LACP active or passive on the port.
To maintain security, LACP is not allowed on ports configured for port security. If you configure port security on a port on which LACP (active or passive) is configured, the switch removes the LACP configuration, displays a notice that LACP is disabled on the port, and enables port security on that port. For Example:
The switch does not allow you to configure LACP on a port on which port security is enabled. For Example:
To restore LACP to the port, you must remove port security and re-enable LACP active or passive.
To convert a trunk from static to dynamic, you must first eliminate the static trunk.
When a port is configured for LACP (active or passive), but does not belong to an existing trunk group, you can add that port to a static trunk. Doing so disables dynamic LACP on that port, which means you must manually configure both ends of the trunk.
You can configure a port for LACP-active or LACP-passive, but on a dynamic LACP trunk you cannot configure the other options that you can on static trunks. If you want to manually configure a trunk, use the trunk command.
A dynamic LACP trunk operates only in the default VLAN (unless you have enabled GVRP on the switch and use Forbid to prevent the ports from joining the default VLAN).
If you want to use LACP for a trunk on a non-default VLAN and GVRP is disabled, configure the trunk as a static trunk.
Some older devices are limited to four ports in a trunk. When eight LACP-enabled ports are connected to one of these older devices, four ports connect, but the other four ports are blocked. The LACP status of the blocked ports is shown as 'Failure.'
If one of the other ports becomes disabled, a blocked port replaces it (Port Status becomes 'Up'). When the other port becomes active again, the replacement port goes back to blocked (Port Status is 'Blocked'). It can take a few seconds for the switch to discover the current status of the ports.
Blocked ports with LACP
If there are ports that you do not want on the default VLAN, ensure that they cannot become dynamic LACP trunk members. Otherwise a traffic loop can unexpectedly occur. For Example:
A dynamic LACP trunk forming in a VLAN can cause a traffic loop
Easy control methods include either disabling LACP on the selected ports or configuring them to operate in static LACP trunks.
If Spanning Tree, IGMP, or both are enabled in the switch, a dynamic LACP trunk operates only with the default settings for these features and does not appear in the port listings for these features.
Half-duplex, different port speeds, or both not allowed in LACP trunks
Theports on both sides of an LACP trunk must be configured for the same speed and for full-duplex (FDx). The 802.3ad LACP standard specifies a full-duplex (FDx) requirement for LACP trunking. (10-gigabit ports operate only at FDx.)
A port configured as LACP passive and not assigned to a port trunk can be configured to half-duplex (HDx). However, in any of the following cases, a port cannot be reconfigured to an HDx setting:
If the port is a 10-gigabit port.
If a port is set to LACP Active, you cannot configure it to HDx.
If a port is already a member of a static or dynamic LACP trunk, you cannot configure it to HDx.
If a port is already set to HDx, the switch does not allow you to configure it for a static or dynamic LACP trunk.
Hp Procurve 802.1 X Configuration Example Software
A port configured for dynamic LACP can properly interoperate with a port configured for static (TrkX) LACP, but any ports configured as standby LACP links are ignored.
VLANs provide a method for segmenting a network into related groups, improving the efficiency of traffic flow, and limiting the propagation of multicast and broadcast messages. On an individual switch, traffic between VLANs is blocked unless the VLANs are connected by a router, increasing security.
A VLAN is a group of ports designated by the switch as belonging to the same broadcast domain. That is, all ports carrying traffic for a particular subnet address would belong to the same VLAN. Using a VLAN, you can group users by logical function instead of physical location. This helps to control bandwidth usage by allowing you to group high-bandwidth users on low-traffic segments and to organize users from different LAN segments according to their need for common resources. Beginning with release C.06.01 of the switch software (operating system, or 'OS') you can use the switch's console interface to configure up to 30 port-based, IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs. (Earlier releases of the OS allow up to eight port-based, IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs.) This enables you to use the same port for two or more VLANs and still allows interoperation with older switches that require a separate port for each VLAN. For more information:
- If you have access to the World Wide Web see HP's ProCurve website at http://www.hp.com/go/procurve.
- If you want a detailed description of how to use and configure VLANs with this switch product, refer to the Management and Configuration Guide (shipped with the switch and also available on HP's Network City website at http://www.hp.com/go/procurve).
Quick Scroll to:
Devices supported:
- HP ProCurve Switch8000M, 4000M, 1600M, 2424M, and 2400M with software update C.08.XX.
Note: If a switch is a Commander, the stack options will appear at the top of the page.
Note: When multiple VLANs exist on a switch, only one VLAN can be untagged for each port. When you first add a VLAN to a switch, the default setting on that VLAN is No for all ports, indicating that no ports are members of this VLAN. Using the Web browser interface, if you then reconfigure a port to Untagged for a new VLAN while there is an Untagged setting on another VLAN for the same port, the switch automatically reconfigures the other VLAN setting to No. For example, if you configure Port A1 as Untagged for the 2nd VLAN, then the switch automatically reconfigures DEFAULT_VLAN for port A1 to No.
How To..
Access the VLAN Configuration Page from HP TopTools
- Click on the Devices button in the navigation frame.
- Select Device Types from the menu.
- Select Networking Devices.
- Double-click on the device in the device list.
- In the Status page click on the Configuration tab. The device's configuration page displays.
- Select the VLAN Configuration button. The VLAN Configuration page displays.
Access the VLAN Configuration page using the Web Agent
- Click on the Configuration tab.
- Select the VLAN Configuration button. The VLAN Configuration page displays.
Enable VLANs
To enable VLANs, click the VLANs Enabled radio button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page.
If you change the current setting, you need to reboot the switch to effect the change. You will be prompted for the reboot.
Add a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Enter a name for the new VLAN in VLAN Name field below the Current VLAN Definitions list box.
- Enter the 802.1Q ID (an unused number between 1 and 4094) in the field labeled 802.1Q VLAN ID.
- Click onthe Add VLAN button. The VLAN appears in the Current VLAN Definitions box.
Rename a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Select the VLAN to be renamed from the Current VLAN Definitions list.
- Enter a name for the selected VLAN in the New VLAN Name field.
- Click on the Rename Selected VLAN button to save the new name.
Remove a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Select the VLAN to remove from the Current VLANS box.
- Click on the Remove Selected VLAN button.
- Confirm removal of the VLAN.
Modify Port VLAN Configuration
To modify ports in a VLAN:
- In the VLAN table, click on the Modify button for the VLAN whose ports you want to modify. The Modify Port VLAN Configuration page displays.
- Select the port to be modified.
- Select the Mode, for example, Tagged.
- Click on the Apply button.
Quickload v 3.9. The modes are:
- Tagged - Each tagged VLAN has a unique VLAN ID (VID). You can configure multiple tagged VLANs on the same port.
- Untagged - The switch allows one untagged VLAN per port.
- No - The port is not a member of that VLAN.
Related Topics
VLAN operation with:
NOTE:LACP requires full-duplex (FDx) links of the same media type (10/100Base-T, 100FX, and so on) and the same speed and enforces speed and duplex conformance across a trunk group. For most installations, HP Switch recommends that you leave the port mode settings at |
LACP trunk status commands include:
| Trunk display method | Static LACP trunk | Dynamic LACP trunk |
|---|---|---|
CLI show lacp command | Included in listing. | Included in listing. |
CLI show trunk command | Included in listing. | Not included. |
| Port/Trunk Settings screen in menu interface | Included in listing. | Not included |
Thus, to display a listing of dynamic LACP trunk ports, you must use the show lacp command.
In most cases, trunks configured for LACP on the switches operate as described in LACP trunk types.
LACP trunk types
| LACP port trunk configuration | Operation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic LACP | This option automatically establishes an 802.3ad-compliant trunk group, with LACP for the port Type parameter and DynX for the port Group name, where X is an automatically assigned value from 1 to 60, depending on how many dynamic and static trunks are currently on the switch. (The switch allows a maximum of 60 trunk groups in any combination of static and dynamic trunks.)
Under the following conditions, the switch automatically establishes a dynamic LACP port trunk group and assigns a port Group name:
Either of the above link configurations allows a dynamic LACP trunk link. Backup Links:A maximum of eight operating links are allowed in the trunk, but, with dynamic LACP, you can configure one or more additional (backup) links that the switch automatically activates if a primary link fails. To configure a link as a standby for an existing eight-port dynamic LACP trunk, ensure that the ports in the standby link are configured as either active-to-active or active-to-passive between switches. Displaying dynamic LACP trunk data: To list the configuration and status for a dynamic LACP trunk, use the CLI
| ||
| Static LACP | Provides a manually configured, static LACP trunk to accommodate these conditions:
The trunk operates if the trunk group on the opposite device is running one of the following trunking protocols: This option uses LACP for the port Type parameter and TrkX for the port Group parameter, where X is an automatically assigned value in a range corresponding to the maximum number of trunks the switch allows. (The table on Trunk types used in static and dynamic trunk groups lists the maximum number of trunk groups allowed on the switches.) Displaying static LACP trunk data : To list the configuration and status for a static LACP trunk, use the CLI Static LACP does not allow standby ports. |
In the default configuration, LACP is disabled for all ports. If LACP is not configured as Active on at least one end of a link, the port does not try to detect a trunk configuration and operates as a standard, untrunked port. LACP port status data lists the elements of per-port LACP operation. To display this data for a switch, execute the following command in the CLI:
LACP port status data
| Status name | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|
| Port Numb | Shows the physical port number for each port configured for LACP operation (C1, C2, C3 …). Unlisted port numbers indicate that the missing ports that are assigned to a static trunk group are not configured for any trunking. | |
| LACP Enabled | Active: The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets. Passive: The port does not automatically send LACP protocol packets and responds only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device. A link having either two active LACP ports or one active port and one passive port can perform dynamic LACP trunking. A link having two passive LACP ports does not perform LACP trunking because both ports are waiting for an LACP protocol packet from the opposite device.
| |
| Trunk Group | TrkX: This port has been manually configured into a static LACP trunk. Trunk group same as port number: The port is configured for LACP, but is not a member of a port trunk. | |
| Port Status | Up: The port has an active LACP link and is not blocked or in standby mode. Down: The port is enabled, but an LACP link is not established. This can indicate, For example, a port that is not connected to the network or a speed mismatch between a pair of linked ports. Disabled: The port cannot carry traffic. Blocked: LACP, Spanning Tree has blocked the port. (The port is not in LACP standby mode.) This may be caused by a (brief) trunk negotiation or a configuration error, such as differing port speeds on the same link or trying to connect the switch to more trunks than it can support. (See the table on Trunk configuration protocols.)
Standby: The port is configured for dynamic LACP trunking to another device, but the maximum number of ports for the dynamic trunk to that device has already been reached on either the switch or the other device. This port will remain in reserve, or 'standby' unless LACP detects that another, active link in the trunk has become disabled, blocked, or down. In this case, LACP automatically assigns a standby port, if available, to replace the failed port. | |
| LACP Partner | Yes: LACP is enabled on both ends of the link. No: LACP is enabled on the switch, but either LACP is not enabled or the link has not been detected on the opposite device. | |
| LACP Status | Success: LACP is enabled on the port, detects and synchronizes with a device on the other end of the link, and can move traffic across the link. Failure: LACP is enabled on a port and detects a device on the other end of the link, but is not able to synchronize with this device, and therefore is not able to send LACP packets across the link. This can be caused, For example, by an intervening device on the link (such as a hub), a bad hardware connection, or if the LACP operation on the opposite device does not comply with the IEEE 802.3ad standard. |
802.1X (Port-based access control) configured on a port
To maintain security, LACP is not allowed on ports configured for 802.1X authenticator operation. Chaos uk discography. If you configure port security on a port on which LACP (active or passive) is configured, the switch removes the LACP configuration, displays a notice that LACP is disabled on the port, and enables 802.1X on that port.
Hp Switch 802.1 X Configuration
The switch does not allow you to configure LACP on a port on which port access (802.1X) is enabled. For Example:
To restore LACP to the port, you must first remove the 802.1X configuration of the port and then re-enable LACP active or passive on the port.
To maintain security, LACP is not allowed on ports configured for port security. If you configure port security on a port on which LACP (active or passive) is configured, the switch removes the LACP configuration, displays a notice that LACP is disabled on the port, and enables port security on that port. For Example:
The switch does not allow you to configure LACP on a port on which port security is enabled. For Example:
To restore LACP to the port, you must remove port security and re-enable LACP active or passive.
To convert a trunk from static to dynamic, you must first eliminate the static trunk.
When a port is configured for LACP (active or passive), but does not belong to an existing trunk group, you can add that port to a static trunk. Doing so disables dynamic LACP on that port, which means you must manually configure both ends of the trunk.
You can configure a port for LACP-active or LACP-passive, but on a dynamic LACP trunk you cannot configure the other options that you can on static trunks. If you want to manually configure a trunk, use the trunk command.
A dynamic LACP trunk operates only in the default VLAN (unless you have enabled GVRP on the switch and use Forbid to prevent the ports from joining the default VLAN).
If you want to use LACP for a trunk on a non-default VLAN and GVRP is disabled, configure the trunk as a static trunk.
Some older devices are limited to four ports in a trunk. When eight LACP-enabled ports are connected to one of these older devices, four ports connect, but the other four ports are blocked. The LACP status of the blocked ports is shown as 'Failure.'
If one of the other ports becomes disabled, a blocked port replaces it (Port Status becomes 'Up'). When the other port becomes active again, the replacement port goes back to blocked (Port Status is 'Blocked'). It can take a few seconds for the switch to discover the current status of the ports.
Blocked ports with LACP
If there are ports that you do not want on the default VLAN, ensure that they cannot become dynamic LACP trunk members. Otherwise a traffic loop can unexpectedly occur. For Example:
A dynamic LACP trunk forming in a VLAN can cause a traffic loop
Easy control methods include either disabling LACP on the selected ports or configuring them to operate in static LACP trunks.
If Spanning Tree, IGMP, or both are enabled in the switch, a dynamic LACP trunk operates only with the default settings for these features and does not appear in the port listings for these features.
Half-duplex, different port speeds, or both not allowed in LACP trunks
Theports on both sides of an LACP trunk must be configured for the same speed and for full-duplex (FDx). The 802.3ad LACP standard specifies a full-duplex (FDx) requirement for LACP trunking. (10-gigabit ports operate only at FDx.)
A port configured as LACP passive and not assigned to a port trunk can be configured to half-duplex (HDx). However, in any of the following cases, a port cannot be reconfigured to an HDx setting:
If the port is a 10-gigabit port.
If a port is set to LACP Active, you cannot configure it to HDx.
If a port is already a member of a static or dynamic LACP trunk, you cannot configure it to HDx.
If a port is already set to HDx, the switch does not allow you to configure it for a static or dynamic LACP trunk.
Hp Procurve 802.1 X Configuration Example Software
A port configured for dynamic LACP can properly interoperate with a port configured for static (TrkX) LACP, but any ports configured as standby LACP links are ignored.
VLANs provide a method for segmenting a network into related groups, improving the efficiency of traffic flow, and limiting the propagation of multicast and broadcast messages. On an individual switch, traffic between VLANs is blocked unless the VLANs are connected by a router, increasing security.
A VLAN is a group of ports designated by the switch as belonging to the same broadcast domain. That is, all ports carrying traffic for a particular subnet address would belong to the same VLAN. Using a VLAN, you can group users by logical function instead of physical location. This helps to control bandwidth usage by allowing you to group high-bandwidth users on low-traffic segments and to organize users from different LAN segments according to their need for common resources. Beginning with release C.06.01 of the switch software (operating system, or 'OS') you can use the switch's console interface to configure up to 30 port-based, IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs. (Earlier releases of the OS allow up to eight port-based, IEEE 802.1Q-compliant VLANs.) This enables you to use the same port for two or more VLANs and still allows interoperation with older switches that require a separate port for each VLAN. For more information:
- If you have access to the World Wide Web see HP's ProCurve website at http://www.hp.com/go/procurve.
- If you want a detailed description of how to use and configure VLANs with this switch product, refer to the Management and Configuration Guide (shipped with the switch and also available on HP's Network City website at http://www.hp.com/go/procurve).
Quick Scroll to:
Devices supported:
- HP ProCurve Switch8000M, 4000M, 1600M, 2424M, and 2400M with software update C.08.XX.
Note: If a switch is a Commander, the stack options will appear at the top of the page.
Note: When multiple VLANs exist on a switch, only one VLAN can be untagged for each port. When you first add a VLAN to a switch, the default setting on that VLAN is No for all ports, indicating that no ports are members of this VLAN. Using the Web browser interface, if you then reconfigure a port to Untagged for a new VLAN while there is an Untagged setting on another VLAN for the same port, the switch automatically reconfigures the other VLAN setting to No. For example, if you configure Port A1 as Untagged for the 2nd VLAN, then the switch automatically reconfigures DEFAULT_VLAN for port A1 to No.
How To..
Access the VLAN Configuration Page from HP TopTools
- Click on the Devices button in the navigation frame.
- Select Device Types from the menu.
- Select Networking Devices.
- Double-click on the device in the device list.
- In the Status page click on the Configuration tab. The device's configuration page displays.
- Select the VLAN Configuration button. The VLAN Configuration page displays.
Access the VLAN Configuration page using the Web Agent
- Click on the Configuration tab.
- Select the VLAN Configuration button. The VLAN Configuration page displays.
Enable VLANs
To enable VLANs, click the VLANs Enabled radio button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page.
If you change the current setting, you need to reboot the switch to effect the change. You will be prompted for the reboot.
Add a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Enter a name for the new VLAN in VLAN Name field below the Current VLAN Definitions list box.
- Enter the 802.1Q ID (an unused number between 1 and 4094) in the field labeled 802.1Q VLAN ID.
- Click onthe Add VLAN button. The VLAN appears in the Current VLAN Definitions box.
Rename a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Select the VLAN to be renamed from the Current VLAN Definitions list.
- Enter a name for the selected VLAN in the New VLAN Name field.
- Click on the Rename Selected VLAN button to save the new name.
Remove a VLAN
- Click on the Add/Remove VLANs button at the bottom of the table in the VLAN Configuration page. The Add/Remove VLAN page displays.
- Select the VLAN to remove from the Current VLANS box.
- Click on the Remove Selected VLAN button.
- Confirm removal of the VLAN.
Modify Port VLAN Configuration
To modify ports in a VLAN:
- In the VLAN table, click on the Modify button for the VLAN whose ports you want to modify. The Modify Port VLAN Configuration page displays.
- Select the port to be modified.
- Select the Mode, for example, Tagged.
- Click on the Apply button.
Quickload v 3.9. The modes are:
- Tagged - Each tagged VLAN has a unique VLAN ID (VID). You can configure multiple tagged VLANs on the same port.
- Untagged - The switch allows one untagged VLAN per port.
- No - The port is not a member of that VLAN.
Related Topics
VLAN operation with:
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Automatic Broadcast Control (ABC)
- IP Multicast (IGMP)
Copyright © 2000 by Hewlett-Packard Company
